Introduction to ERP: Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning
In today’s competitive world, businesses rely on technology to manage their operations more effectively. One of the most powerful tools for this is ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). But many people still ask, “What is ERP and why is it important for organizations?” ERP is a system that integrates different business processes into one platform, helping enterprises plan their resources, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. From finance and HR to production and sales, ERP plays a central role in running modern businesses.

What is ERP and How Does It Work?
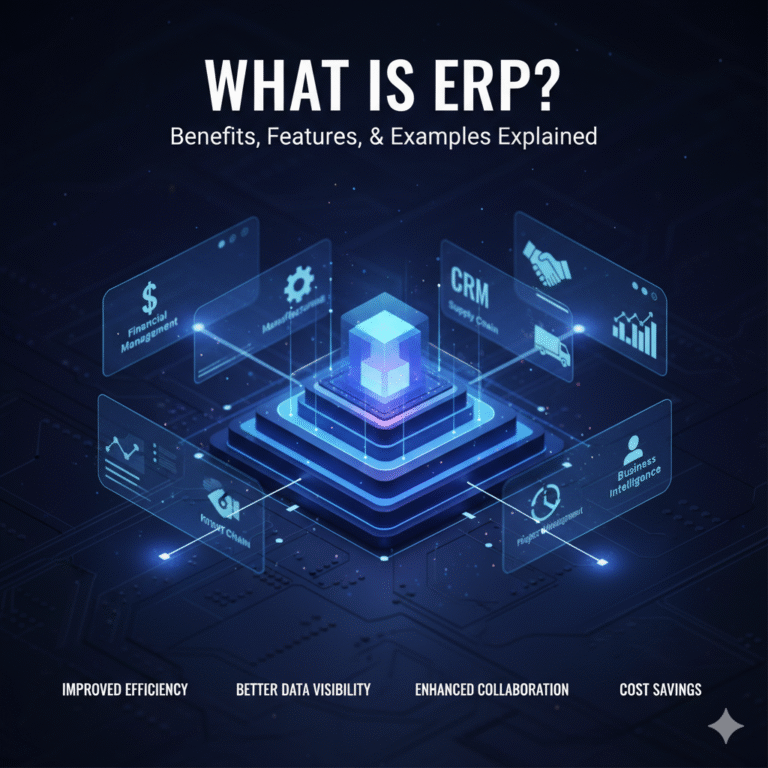
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, a business management system that helps organizations plan, manage, and integrate their resources effectively. By connecting different departments such as finance, HR, production, and sales, ERP ensures smooth operations and better decision-making. The main goal of ERP is to increase productivity, efficiency, and profitability across the enterprise.
What is an Enterprise in ERP?
An enterprise is a large organization that manages huge resources such as people, money, machines, and methods. To handle these diverse resources effectively, enterprises rely on ERP systems. With ERP, enterprises can align their processes, reduce duplication of work, and achieve long-term growth through streamlined operations.
Key Resources Managed by ERP Systems
The core resources of an enterprise include money, men, materials, machines, marketing, methods, and management. Each resource plays a vital role in business success. ERP integrates all these resources into a single system, ensuring better planning and utilization, which ultimately leads to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Top Benefits of Implementing an ERP System
Implementing an ERP system provides several benefits such as eliminating data duplication, reducing redundancy, and delivering real-time business insights. ERP improves productivity, enhances customer satisfaction, and ensures a higher return on investment (ROI). It also allows businesses to respond faster to changing market needs.
Main Characteristics of ERP Systems
Key characteristics of ERP systems include a single uniform platform across the organization, integration of multiple departments, and support for various languages and currencies. These features make ERP suitable for global enterprises, helping them operate seamlessly across countries and industries.
List of Popular ERP Systems in the Market
There are many ERP systems available in the market, such as SAP, Oracle Financials, PeopleSoft, JD Edwards, Ramco Marshal, Baan, and Cyber. Among them, SAP dominates with more than 90% of the ERP market share due to its ability to adapt to the requirements of industries worldwide.
Why SAP Leads the ERP Market
When it comes to ERP solutions, SAP is the global market leader, trusted by businesses of all sizes and industries. More than 90% of Fortune 500 companies use SAP to manage their operations efficiently. The reason for SAP’s dominance lies in its adaptability, scalability, and ability to meet the complex needs of enterprises worldwide.
SAP was designed after studying the operations of industries across the globe. This deep understanding helped the software developers create a system that fits businesses of every sector—from manufacturing and retail to healthcare and finance. As a result, SAP ERP is known for its industry-specific solutions and flexibility.
Another reason why SAP leads the ERP market is its integration capabilities. Unlike many other systems, SAP allows different business modules like finance, procurement, sales, and production to communicate seamlessly. This ensures a single source of truth for data, eliminating duplication and improving decision-making.
SAP also supports global enterprises by offering multi-language and multi-currency functionality. This makes it an ideal choice for companies operating in multiple countries. Its ability to handle compliance, taxation, and legal requirements across regions is unmatched in the ERP world.
In addition, SAP invests heavily in innovation. With SAP S/4HANA powered by in-memory computing, businesses now gain real-time insights, faster processing, and advanced analytics. These technological advancements make SAP not only reliable but also future-ready, which is why it continues to dominate the ERP landscape.
Conclusion: Why Every Business Needs ERP
In today’s competitive world, every business needs ERP to stay efficient and profitable. Without a centralized system, organizations often struggle with duplicated data, disconnected processes, and slow decision-making. ERP solves these challenges by integrating every department into one unified platform.
Whether it’s managing finances, handling procurement, or tracking production, ERP ensures that all business operations run smoothly. This not only saves time but also reduces costs and improves productivity. By streamlining workflows, businesses can focus more on growth and less on manual errors.
Another major reason why ERP is essential is its ability to provide real-time information. Business leaders no longer need to wait for reports to be compiled—they can access accurate data instantly. This empowers decision-makers to respond quickly to market changes and customer needs.
ERP systems also improve customer satisfaction. With better visibility into inventory, sales, and supply chain, companies can fulfill orders faster and maintain stronger relationships with clients. In a customer-driven market, this becomes a significant advantage.
Ultimately, ERP is not just a software—it is a strategic tool for success. From small businesses to multinational enterprises, ERP helps organizations achieve efficiency, growth, and long-term profitability. This is why ERP has become a necessity, not a luxury, for modern businesses.