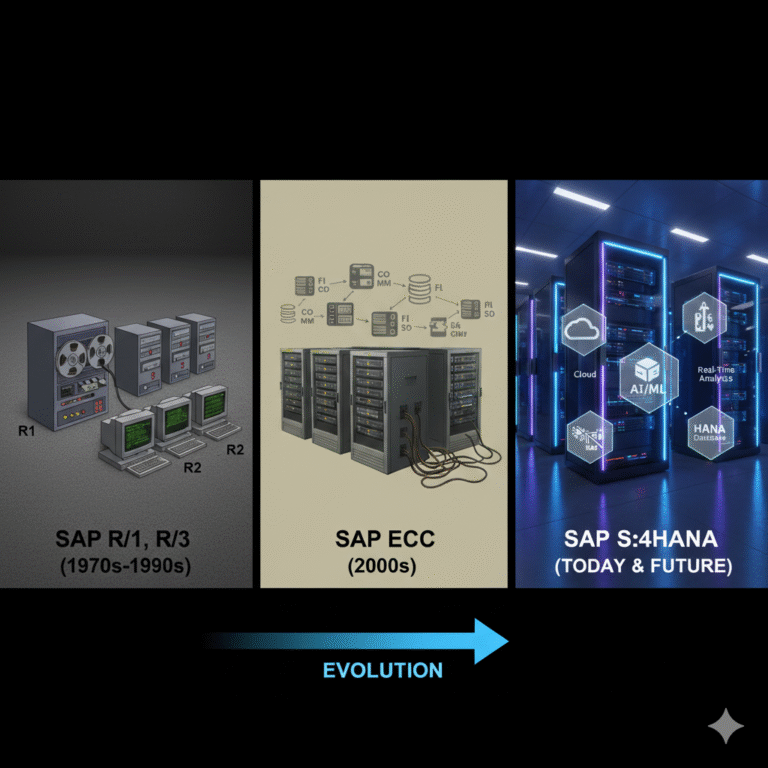
Discover the deferance between ECC and S4HANA with a clear look at SAP R1, R2, and R3 evolution. Learn how SAP ERP has transformed over time.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to SAP ERP Evolution
SAP has been a pioneer in ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems for decades. From its early versions R1, R2, and R3 to modern ERP solutions, SAP has constantly evolved to meet changing business needs. One of the most asked questions today is about the deferance between ECC and S4HANA, and how these versions fit into SAP’s overall journey. Understanding this transition helps businesses prepare for the future of digital transformation.

SAP R1, R2, R3 – The Foundation of ERP
SAP R1 – The Beginning of ERP (1970s)
SAP R1 (Real-Time 1) was the first version of SAP launched in the 1970s. It was a single-tier architecture designed for financial accounting. Though limited, it laid the foundation for ERP systems.
SAP R2 – Mainframe-Based ERP (1980s)
In the 1980s, SAP introduced R2, a mainframe-based ERP system. It supported multiple business processes like materials management and production planning. This was the first step toward integrating enterprise functions.
SAP R3 – Client-Server Revolution (1990s)
SAP R3 marked a big leap with client-server architecture. It allowed businesses to use ERP on different machines (application server, database server, and client). This made ERP more flexible and scalable, driving global adoption.
SAP ECC (ERP Central Component)
What is SAP ECC?
SAP ECC (ERP Central Component) was introduced in the early 2000s as part of SAP Business Suite. It became one of the most widely used ERP systems worldwide.
Key Features of SAP ECC
Supports modules like FI (Finance), CO (Controlling), MM (Materials Management), SD (Sales & Distribution), HR, and more.
Relies on traditional databases like Oracle, IBM DB2, or Microsoft SQL.
Strong customization options to fit business needs.
Limitations of ECC in the Modern Era
While powerful, ECC struggles with today’s real-time data needs. Reports are slower, the user interface is outdated, and it relies on older databases rather than in-memory processing.
SAP S/4HANA – The Next-Generation ERP
What is SAP S4HANA?
SAP S/4HANA, launched in 2015, is the latest ERP suite built on the SAP HANA in-memory database. It is designed for speed, real-time analytics, and simplified processes.
Key Features and Benefits of S/4HANA
Uses HANA database for lightning-fast performance.
Offers Fiori user interface (UI) for a modern, user-friendly experience.
Simplifies data models and processes.
Provides real-time reporting and predictive analytics.
Available in on-premise, cloud, and hybrid deployments.
Why SAP Moved from ECC to S4HANA
The shift was necessary to support digital business models, IoT, AI, and big data. ECC could not handle such requirements effectively, making S4HANA the future-proof solution.
Deferance Between ECC and S4HANA
Technical Deferances
ECC supports multiple databases; S4HANA runs only on HANA.
ECC has batch-based reporting; S4HANA offers real-time analytics.
ECC uses older GUIs; S4HANA uses Fiori (web-based, mobile-friendly).
Functional Deferances
S4HANA has simplified processes (e.g., fewer tables in finance).
ECC requires more complex configurations.
S4HANA integrates advanced analytics and AI features.
Deployment Deferances
ECC is mainly on-premise.
S4HANA offers on-premise, cloud, and hybrid flexibility.
ECC vs S4HANA – Migration Insights
Challenges in Migrating
High migration cost and effort.
Need for staff training on new features.
System downtime during migration.
Advantages of Moving to S/4HANA
Improved performance with in-memory computing.
Simplified IT landscape and reduced costs.
Future-ready ERP with AI, IoT, and cloud capabilities.
Future of SAP ERP Systems
SAP has announced the end of ECC support by 2027, which makes migration to S4HANA critical for businesses wanting long-term support.
| Feature | SAP ECC | SAP S/4HANA |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Oracle, IBM, SQL, etc. | Only SAP HANA (in-memory) |
| Reporting | Batch-based, slower | Real-time analytics |
| User Interface | SAP GUI | SAP Fiori (modern, mobile) |
| Deployment | On-premise only | On-premise, Cloud, Hybrid |
| Data Model | Complex, many tables | Simplified, fewer tables |
| Innovation Support | Limited | Supports AI, IoT, Big Data |
FAQs on Deferance Between ECC and S4HANA
Q1: What is the main deferance between ECC and S4HANA?
The main deferance is that ECC supports multiple databases, while S4HANA only runs on the in-memory HANA database for faster performance.
Q2: Why is SAP ECC being replaced?
SAP ECC is outdated and cannot handle real-time, AI-driven business needs. S4HANA is built for the digital era.
Q3: Can companies still use ECC after 2027?
SAP will stop mainstream support for ECC in 2027, but extended support is available till 2030 (with higher costs).
Q4: What is the future of SAP S/4HANA?
S4HANA is the future of SAP ERP, offering integration with AI, machine learning, IoT, and cloud platforms.
Conclusion
The deferance between ECC and S4HANA is not just technical—it represents a complete shift in how businesses use ERP. From the early days of SAP R1, R2, and R3 to ECC and now S4HANA, SAP has continuously evolved to meet enterprise needs. Migrating to S4HANA is not just an upgrade; it’s a step toward digital transformation and future-ready business operations.
🚀 Level Up Your Learning
Be the first to explore ERP, SAP, and tech tutorials from ErpediaEdu.
One click. Unlimited growth.